What is Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic Retinopathy is a diabetes-related eye condition that affects the tiny blood vessels of the retina. Elevated blood sugar levels can cause these vessels to weaken, leak, or swell, leading to macular edema. In advanced stages, abnormal new blood vessels may form and bleed, a serious condition known as Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR), which can threaten vision if left untreated.
At Motewar Netralaya, Nanded, patients receive advanced diagnosis and treatment for Diabetic Retinopathy to help protect and preserve their eyesight. Dr. Vivek Motewar – 21+ years experienced eye doctor in Nanded is dedicated to providing comprehensive, patient-focused eye care with modern technology and proven treatment approaches.
Key Facts:
- The risk and severity of Diabetic Retinopathy increase with the duration of diabetes.
- After 10 years of diabetes, around 50% of patients develop DR.
- After 20 years, this risk rises to about 90%.
- Regular eye checkups every 6–12 months can detect early changes and help prevent blindness.
Symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy
In its early stages, diabetic retinopathy often causes no symptoms or noticeable vision loss. However, if left untreated, the condition can progressively worsen, potentially leading to significant vision impairment or even blindness. Early warning signs may include:
- Blurred or distorted vision
- Seeing floaters (spots or dark strings)
- Flashes of light
- Sudden and unexpected vision loss
Test And Diagnosis
Macular edema and proliferative diabetic retinopathy are typically detected through a dilated eye examination. Additional tests may include:
- Fluorescein Angiography – to assess blood vessel leakage and abnormal growth.
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) – to measure retinal thickness and detect swelling.
In some cases, advanced retinal damage can occur without the patient noticing any changes in vision. Since most treatments for diabetic eye disease are more effective at preventing and slowing progression rather than reversing advanced damage, regular comprehensive eye exams—including pupil dilation—are essential for all individuals with diabetes.
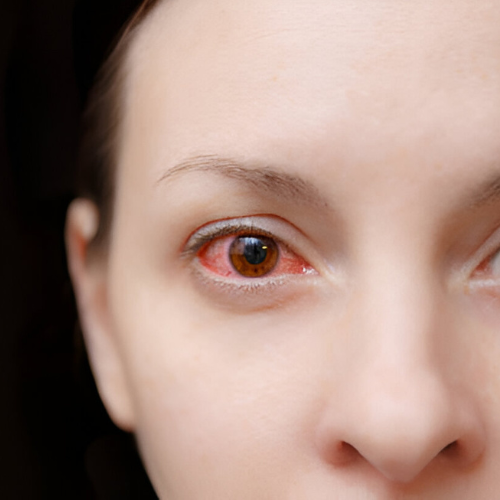
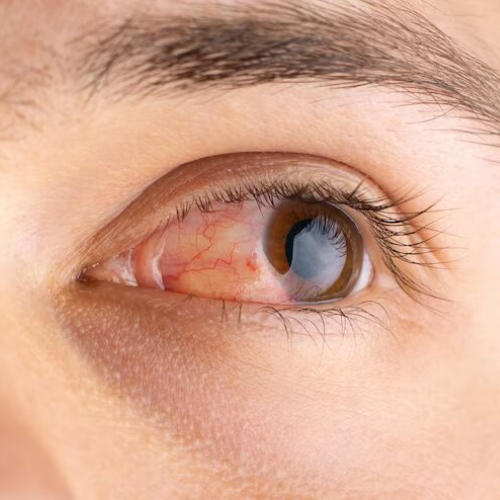
How Is Diabetic Retinopathy Treated?
Treatment and Drugs
In its early stages, diabetic retinopathy may not require active medical treatment. However, regular eye examinations are essential to monitor disease progression. Maintaining strict control of blood sugar and blood pressure can significantly slow down or even prevent the development of diabetic retinopathy.
In more advanced stages, timely treatment is necessary to halt further damage, prevent vision loss, and, in some cases, restore vision.
Treatment options include:
1.Anti-VEGF Therapy (Avastin, Lucentis, Ozurdex)
- This involves injecting medication directly into the back of the eye.
- The drug is an antibody that binds to and neutralizes excess VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor), which drives abnormal blood vessel growth and leakage.
- Lucentis is FDA-approved for macular edema. Avastin and Ozurdex are also commonly used options.
2.Intraocular Steroid Injection
- Steroid injections into the eye help reduce swelling in the retina (macular edema) and improve vision.
3. Retinal Laser Therapy
- How it works: Laser energy seals leaking blood vessels, shrinks abnormal ones, and reduces the risk of further bleeding.
- This helps stabilize vision and prevent additional retinal damage.
Technique of Laser Therapy for Diabetic Retinopathy
Laser therapy is performed as an outpatient procedure, so hospital admission is not necessary. The patient is seated at a slit lamp—similar to the one used in a regular eye examination but specially adapted with a laser fibreoptic system. Numbing eye drops are applied to the cornea, and a therapeutic contact lens is gently placed on the eye.
During the session, the patient may see bright flashes of light but usually feels no pain. It is important to keep the eye as still as possible to ensure precise laser application and avoid damage to the fovea. A typical session lasts about 10 minutes.
The patient can speak to the ophthalmologist at any time during the procedure if there is any discomfort, allowing the treatment to be paused safely. After the session, it is common to feel dazzled or to notice the laser spots in vision—these usually fade within a few days. No special precautions are generally needed afterward, although additional eye drops or oral medication may be prescribed in certain cases.
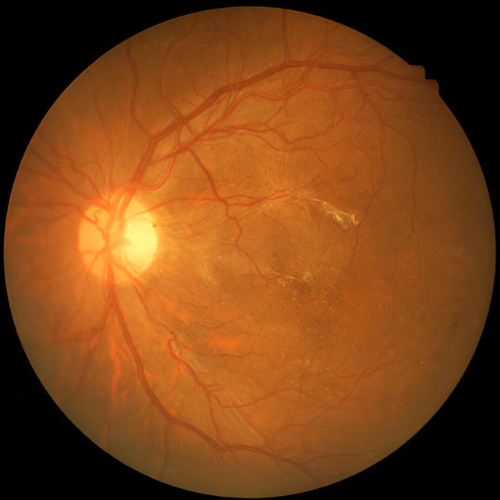
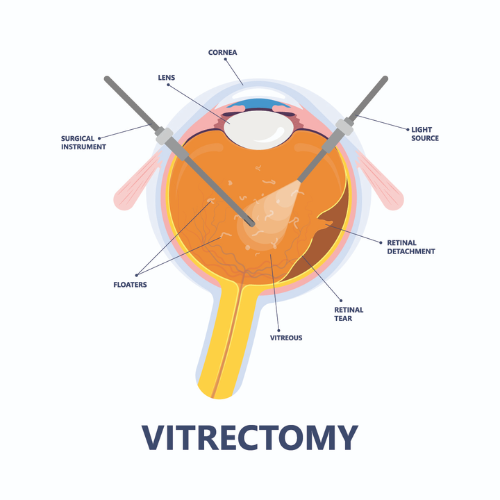
Vitrectomy
In advanced cases of proliferative diabetic retinopathy, a vitrectomy may be advised. This delicate microsurgical procedure is performed in the operating room to remove the vitreous gel that has become clouded or filled with blood, and replace it with a clear solution. If scar tissue has caused the retina to detach from the back of the eye, additional retinal repair is carried out during the same surgery. Without timely intervention, retinal detachment can lead to severe vision loss or even permanent blindness.
Retinal Vein Occlusion
Retinal vein occlusion occurs when one of the tiny retinal veins becomes blocked by a blood clot.Risk factors, apart from advanced age and genetic factors, are smoking, obesity, high blood pressure, diabetes and high cholesterol levels..The occlusion of the vein prevents the drainage of blood which results in haemorrhages and a swelling of the surrounding retina. In the long run the retina is irreversibly damaged.
There Are Two Main Types of Retinal Vein Occlusion?
- Branch retinal vein occlusion
- Central retinal vein occlusion
How Common Is Retinal Vein Occlusion And Who Gets It?
Retinal vein occlusion is a fairly common cause of vision loss. It is most common in people over the age of 60 and it seems to affect both sexes equally.
What Causes Retinal Vein Occlusion?
The exact reason why a blood clot may form in one of the retinal veins is not clear. However, there are some things that are thought to increase your risk of developing retinal vein occlusion. They include the following
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Smoking
- Cardiac diseases (heart related diseases)
- Raised intraocular pressure (glaucoma)
What Are The Possible Complications Of Retinal Vein Occlusion?
Macular oedema: This is swelling of the macula at the centre of the retina.
Neovascularisation: This is abnormal new blood vessel formation at the back of the eye. About one third of people with retinal vein occlusion develop this problem which can sometimes lead to increased pressure within the eye and to glaucoma. Also, the new blood vessels are of a poor quality and can sometimes bleed.
What Are The Symptoms OF Retinal Vein Occlusion?
If you have retinal vein occlusion, you will usually notice painless decrease in vision in one eye or blind spot in one eye. Depending on the severity and also the degree of involvement of the macula, retinal vein occlusions may cause only mild visual loss. However, in some cases they may cause very profound visual loss.
How Is Retinal Vein Occlusion Diagnosed?
Retinal vein occlusion is usually diagnosed after an eye specialist (an ophthalmologist) examines the back of your eye, using an ophthalmoscope. The retina at the back of your eye has a typical appearance in retinal vein occlusion. Your specialist may advise some other tests or examinations to help to see how much damage has occurred to your retina. The tests may include:
- Special photographs of your retina.
- Fluorescein angiography
- Optical coherence tomography
What Is The Treatment For Retinal Vein Occlusion?
Currently, there is no treatment that can reverse the blocked vein. The aims of treatment are to detect and treat any underlying risk factors for the condition and also to detect and treat any complications where possible.
Treatment of any complications
Someone with retinal vein occlusion needs close follow-up so that any complications can be picked up early and treated where possible.
Anti-VEGF therapy (Avastin, Lucentis, Ozurdex)
Anti-VEGF therapy involves the injection of the medication into the back of your eye. The medication is an antibody designed to bind to and remove the excess VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) present in the eye that is causing the disease state. The FDA has approved Lucentis for macular edema and additional treatment options include Avastin and Ozurdex.
What Is The Outlook(Prognosis)?
Following a retinal vein occlusion you are likely to be left with some visual loss. The extent of the visual loss can vary greatly, depending on the severity and exact site of the vein occlusion. Early diagnosis and treatment of retinal vein occlusion and any complications may make a difference to the eventual level of visual loss. However, severe vein occlusions can cause permanent visual loss, even if treated very early. Retinal vein occlusion will recur in about 1 in 6 people (either in the same eye or in the other eye) over the five years.
Frequently Asked Questions
Diabetic eye diseases include diabetic retinopathy, diabetic macular edema (DME), and other conditions that affect the eyes due to diabetes.
Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes that damages blood vessels in the retina, leading to vision problems and, if left untreated, potentially blindness.
Treatment may include laser therapy, intravitreal injections, or in advanced cases, surgery. Early detection and management of diabetes and regular eye examinations are crucial for preventing vision loss.
Diabetic patients should have a comprehensive eye examination at least once a year, or as recommended by their eye care professional. Regular screenings are essential for early detection and timely management of diabetic eye diseases.

Motewar Netralaya
Eye Services – That You Can Trust
Cataract and Premium Lens Implant
We offer advanced cataract removal using the latest phacoemulsification technology, ensuring maximum safety, precision, and effectiveness, along with premium lens implant options for enhanced vision quality.
Children’s Eye Check-up
Children should ideally have their eyes examined between the ages of 5 and 6. An eye check-up becomes essential if your child shows signs such as excessive watering, eye discharge, squint, or difficulty in reading.
Glaucoma Screening
Diabetic eye disease is one of the leading causes of blindness in India. Our centre is fully equipped to diagnose and treat all types of retinal conditions, offering advanced medical care and surgical solutions.
Comprehensive Eye Examination
Experience a fully computerized and automated eye check-up using the advanced TOPCON Phoropter—offering precision, accuracy, and the latest in cutting-edge vision testing technology.
WHY CHOOSE Motewar Netralaya For Glaucoma Treatment in Nanded
Motewar Netralaya is staffed by a team of two highly experienced surgical ophthalmologists. In addition to providing routine eye care, their expertise extends to advanced procedures including vitreoretinal surgeries, laser treatments, and corneal surgeries.
Our hospital is backed by a team of skilled and experienced optometrists, nursing professionals, and trained machine operators who work hand-in-hand with our doctors. In addition, our non-medical staff is well-trained in hospital operations and patient care, ensuring smooth and efficient service at every step.
At Motewar Netralaya, we understand that medical concerns can bring stress and anxiety. That’s why we strive to maintain a warm and welcoming atmosphere, encouraging patients to feel comfortable, relax, and openly share their concerns.
Motewar Netralaya is equipped with cutting-edge ophthalmic technology, including the MEL-90 — the world’s fastest LASIK machine, YAG laser for treating opacities and performing iridectomies, and the Carl Zeiss Green Laser Visulas. These, along with several other state-of-the-art devices, ensure precision, safety, and superior patient outcomes.
We are located on Doctor's lane, near ST Bus Stand, Doctor Lane, Khadakpura, Nanded, Nanded-Waghala, Maharashtra 431601 in Nanded. By-lanes in the vicinity ensure sufficient parking space.
For the convenience of our patients, we have an in-house optical store and medical shop within the same premises. These facilities provide a one-stop solution, ensuring easy access to eyewear and prescribed medications under one roof.
Contact Motewar Netralaya
Get in touch with Motewar Netralaya for expert eye care and advanced laser treatments.
Request a Consultation
Contact Form
Protect Your Vision – Consult Our Experts at Motewar Netralaya
Contact today and see the difference. if you have any questions call us on 02462 358 953